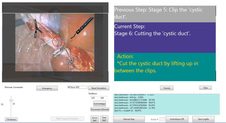
There has been a noticeable increase in the use of virtual reality (VR) simulation technology for medical training of clinical practice. Studies have shown evidence that the use of VR in surgical training improves the practicing of surgical skills, especially for novice trainees. Unfortunately, most available surgical simulators are expensive, with a documented cost ranging between $40K on the low-end to close to $100K. Although there is some evidence showing such simulators can provide the quality of training and testing necessary before a clinical experience for residents, their cost profile makes them unsuitable for use by student populations outside of their training facility.
Given the current climate of budget reductions and reduced allocations to aid hospitals to pay for training of new residents and medical students, we shared the urgent need for the development of effective and low-cost training options to fill in the gap. As such, a low-cost VR surgical simulator was developed and presented in CBMS'13 and CBMS'14.
Given the current climate of budget reductions and reduced allocations to aid hospitals to pay for training of new residents and medical students, we shared the urgent need for the development of effective and low-cost training options to fill in the gap. As such, a low-cost VR surgical simulator was developed and presented in CBMS'13 and CBMS'14.
|
|